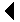
|
|
|
-
Synonyms:
-
Codiolum polyrhizum Lagerheim, Gomontia bornetii Setchell et Gardner, G. caudata Setchell et Gardner, G. habrorhiza Setchell et Gardner
-
Illustrations:
-
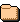
Abbott and Hollenberg 1976, p. 119, fig. 82 ( sporophyte ); Burrows 1991, p. 60, fig. 16 ( sporophytes ); Kornmann 1959, p. 230, fig. 1 ( mature sporophytes with zoospores ), p. 231, fig. 2 ( development of gametophyte from zoospore ), p. 232, fig. 4 ( gametes and syngamy ), p. 233, fig. 5 ( development of sporophyte from zygote ), p. 234, fig. 6 ( gametophytes cultured on mussel shells ), fig. 7 ( sporophytes cultured on mussel shells ), p. 236, fig. 9 ( sporophytes from different mussel shells ); Kornmann 1973, p. 7, fig. 5 ( photos: gametophyte development ), p. 8, fig. 6 ( photos: sporophyte development ); Pedersen 1973, p. 147, fig. 2 e ( photo: discoid gametophyte from nature ); Scagel 1966, pl. 10, fig. A ( gametophytic filament ), figs. B & ndash; D ( sporophyte development ); Setchell and Gardner 1920 b, pl. 18, fig. 1 ( gametophytic filament ), fig. 2 ( sporophytes ), pl. 19, figs. 1, 3 ( sporophytes ), fig. 2 ( gametophytic filaments ); Smith 1944, pl. 1, figs. 8 & ndash; 10 ( sporophytes ); pl. 2, figs. 1, 2, ( sporophytes with simple rhizoids ), figs. 3, 4 ( gametophytic filaments ), figs. 6, 7 ( young sporophytes ), fig. 5 ( mature sporophyte with zoospores ); Wilkinson and Burrows 1972, pl. 1 ( photos ): A ( ring-shaped gametophytes ), B ( early filamentous stage of gametophyte ), C ( floating gametophyte )
-
Life History:
-
uninvestigated in Pacific coast populations; in Europe, alternation of heteromorphic phases, with a vesicular unicellular shell-boring sporophyte that produces quadriflagellate zoospores and a discoid multicellular free-living bisexual gametophyte that produces biflagellate isogametes ( Kornmann 1973; Wilkinson and Burrows 1972; Kornmann 1959 )

-
Note:
-
Wilkinson and Burrows ( 1972 ) showed that six different species have been confused under the name Gomontia polyrhiza . Tha Pacific coast records of this species undoubtedly apply to a variety of entities, including the shell-boring unicellular sporophyte of Monostroma grevillei , which is indistinguishable from the sporophyte of Gomontia polyrhiza . Its identity can be established by culturing.

-
Taxonomy:
-
Burrows 1991, p. 59; Kornmann 1973; Kornmann 1959

|